Various Windows Based FIR Filter And Its Implementation On Audio Signal
1. Type this command on MATLAB prompt:
The GUIDE Quick Start dialog box will show up, as shown in figure below:
2. Select the Blank GUI (Default) template, and then click OK:
3. Drag all components needed, as shown in figure below:
5. You can run the UI. Choose one of signals and then click DRAW button:
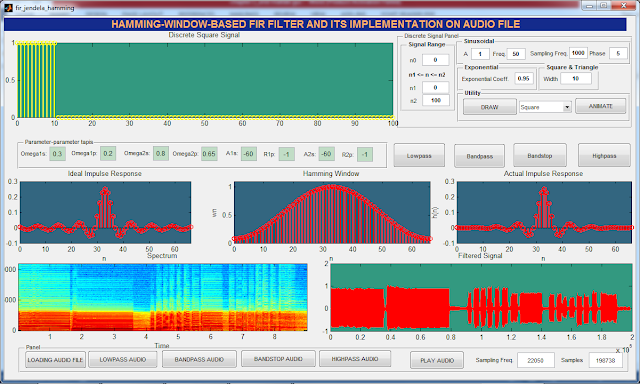
9. You can run the UI. Choose one of signals and then click DRAW button, choose one of window functions, and click on Lowpass button. The result is shown in figure below.
17. You can run the UI. Click LOAD AUDIO FILE button. The result is shown in figure below.
Here, you will build a desktop application (UI, user interface) to simulate how is filtered using FIR filter, Various Windows Based FIR Filter. A number of discrete signals are used as test signals are impulse, step, real exponential, sinusoidal, random, square, angled triangle, equilateral triangle, and trapezoidal signals. In the UI, this FIR filter is used to filter signals and audio file (wav) as well.
Follow these steps below:
1. Type this command on MATLAB prompt:
guide
The GUIDE Quick Start dialog box will show up, as shown in figure below:
2. Select the Blank GUI (Default) template, and then click OK:
3. Drag all components needed, as shown in figure below:
4. Right click on DRAW button and choose View Callbacks and then choose Callback. Define pbDraw_Callback() function below to read signals parameters and displays chosen signal in axes1 component:
% --- Executes on button press in pbDraw. function pbDraw_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pbDraw (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) global n0; global n1; global x; % Reads n0, n1, and n2 n0 = str2num(get(handles.n0,'String')); n1 = str2num(get(handles.n1,'String')); n2 = str2num(get(handles.n2,'String')); exp = str2num(get(handles.expCoef,'String')); % Reads parameters for sinusoidal A = str2num(get(handles.A,'String')); Freq = str2num(get(handles.Freq,'String')); Fase = str2num(get(handles.Phase,'String')); Fs = str2num(get(handles.Fs,'String')); % Reads parameters for square and triangle signals width = str2num(get(handles.width, 'String')); % Choose option from popup menu popupmenusignal1 switch get(handles.popupmenusignal1,'Value') case 1 n = [n1:n2]; x = [(n-n0) == 0]; % Display discrete signal axes(handles.axes1) stem(n,x,'linewidth',2,'color','y'); set(gca,'color',[0.4 0.6 0.5]); title('Discrete Impulse Signal'); case 2 n = [n1:n2]; x = [(n-n0) >= 0]; % Display discrete signal axes(handles.axes1) stem(n,x,'linewidth',2,'color','y'); set(gca,'color',[0.4 0.6 0.5]); title('Discrete Step Signal'); case 3 n = [n1:n2]; x = [(n-n0) >= 0].*[(exp).^(n-n0)]; % Display discrete signal axes(handles.axes1) stem(n,x,'linewidth',1,'color','y'); set(gca,'color',[0.4 0.6 0.5]); title('Discrete Real Exponential Signal'); case 4 n = [n1:n2]; x = [(n-n0) >= 0].*[A*sin(2*pi*(Freq)*((n-n0)/Fs)+Fase)]; % Display discrete signal axes(handles.axes1) stem(n,x,'linewidth',2,'color','y'); set(gca,'color',[0.4 0.6 0.5]); title('Discrete Sinusoidal Signal'); case 5 n = [n1:n2]; x = [(n-n0) >= 0].*(rand(1,(n2-n1+1))-0.5); % Display discrete signal axes(handles.axes1) stem(n,x,'linewidth',1,'color','y'); set(gca,'color',[0.4 0.6 0.5]); title('Discrete Random Signal'); case 6 n = [n1:n2]; x = [(n-n0) >= 0]; ny = [n1:n2]; xy = [(ny-width-n0-1) >= 0]; x = x - xy; % Display discrete signal axes(handles.axes1) stem(n,x,'linewidth',1,'color','y'); set(gca,'color',[0.4 0.6 0.5]); title('Discrete Square Signal'); case 7 n = [n1:n2]; x = n.*[n >= 0]; ny = [n1:n2]; xy = ny.*[(ny-width-1) >= 0]; x = (x - xy)/width; nb = [n1+n0:n2+n0]; % Reads signal range set(handles.n1,'string',(n1+n0)); set(handles.n2,'string',(n2+n0)); % Display discrete signal axes(handles.axes1) stem(nb,x,'linewidth',1,'color','y'); set(gca,'color',[0.4 0.6 0.5]); title('Discrete Angled Triangle Signal'); case 8 n = [n1:n2]; x = n.*[n >= 0]; x2 = [zeros(1,width), x(1:end-width)]; x1 = -x; x1 = [zeros(1,0.5*width), x1(1:end-0.5*width)]; nb1 = n1+n0; nb2 = n2+n0; nb = [nb1:nb2]; % Read signal range set(handles.n1,'string',(nb1)); set(handles.n2,'string',(nb2)); % Returns discrete equilateral triangle signal x = (x + 2*x1+x2)/(0.5*width); % Display discrete signal axes(handles.axes1) stem(nb,x,'linewidth',1,'color','y'); set(gca,'color',[0.4 0.6 0.5]); title('Discrete Equilateral Triangle Signal'); case 9 n = [n1:n2]; x = n.*[n >= 0]; x2 = [zeros(1,width), x(1:end-width)]; x3 = [zeros(1,3*width), x(1:end-3*width)]; x1 = x; x1 = [zeros(1,2*width), x1(1:end-2*width)]; nb1 = n1+n0; nb2 = n2+n0; nb = [nb1:nb2]; % Reads signal range set(handles.n1,'string',(nb1)); set(handles.n2,'string',(nb2)); % Returns discrete trapezoidal signal x = (x - x2 - x1 + x3)/width; % Display discrete signal axes(handles.axes1) stem(nb,x,'linewidth',1,'color','y'); set(gca,'color',[0.4 0.6 0.5]); title('Discrete Trapezoidal Signal');
end
5. You can run the UI. Choose one of signals and then click DRAW button:
6. Set the String property of popupmenuwindow with Rectangular, Bartlett, Hann, Hamming, Blackman, and Kaiser.
7. Define ideal_lp() function (save to m file) to calculate ideal lowpass filter, given the cutoff frequency and filter length:
function hd = ideal_lp(wc,M) % Calculates ideal lowpass filter % ------------------------- % [hd]= lp_ideal(wc,M) % wc = cutoff frequency in radian % M = ideal filter length % alpha = (M-1)/2; n = [0:1:(M-1)]; m = n - alpha; fc = wc/pi; hd = fc*sinc(fc*m);
8. Right click on Lowpass button and choose View Callbacks and then choose Callback. Define pbLowpass_Callback() function below to read signals parameters and displays ideal lowpass impulse response, window function (based on window chosen from popupmenuwindow component), actual lowpass impulse response, lowpass magnitude response, and filtered signal:
% --- Executes on button press in pbLowpass. function pbLowpass_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pbLowpass (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) global x; % Reads all filter spesifications As = str2num(get(handles.As,'String')); ws = str2num(get(handles.omega_s,'String')); Rp = str2num(get(handles.Rp,'String')); wp = str2num(get(handles.omega_p,'String')); ws=ws*pi; wp=wp*pi; bandwidth = ws - wp; M = ceil(6.6*pi/bandwidth) + 1; n=[0:1:M-1]; wc = (ws+wp)/2; % cutoff frequency of LPF % Choosing option from popup menu switch get(handles.popupmenuwindow,'Value') case 1 j=boxcar(M); case 2 j=bartlett(M); case 3 j=hann(M); case 4 j=hamming(M); case 5 j=blackman(M); case 6 beta = 0.1102*(As-8.7); j=kaiser(M,beta); end hd = ideal_lp(wc,M); h = hd' .* j; [db,mag,pha,grd,w] = freqz_m(h,[1]); delta_w = 2*pi/1000; % Actual ripple passband Rp = -(min(db(1:1:wp/delta_w+1))); % Minimal stopband attenuation As = -round(max(db(ws/delta_w+1:1:501))); axes(handles.axes7); stem(n,hd, 'color','w'); title('Ideal Lowpass Impulse Response') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axis([0 M-1 min(hd) max(hd)]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('hd(n)') axes(handles.axes8); stem(n,j,'color','w');title('Window Function') axis([0 M-1 0 1.1]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('w(n)') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axes(handles.axes9); stem(n,h,'color','w');title('Actual Lowpass Impulse') axis([0 M-1 min(h) max(h)]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('h(n)') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axes(handles.axes3); plot(w/pi,db, 'linewidth',2,'color','y'); title('Magnitude Response in dB');grid axis([0 1 min(db) max(db)]); xlabel('Frequency in pi unit'); ylabel('dB') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); % Calculates filtered signal y = conv(double(x),double(h), 'same'); axes(handles.axes2); t = 0:length(y)-1; stem(t,y,'linewidth',1,'color','g'); title('Filtered Signal') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]);
9. You can run the UI. Choose one of signals and then click DRAW button, choose one of window functions, and click on Lowpass button. The result is shown in figure below.
10. Right click on Highpass button and choose View Callbacks and then choose Callback. Define pbHighpass_Callback() function below to read signals parameters and displays ideal highpass impulse response, window function (based on window chosen from popupmenuwindow component), actual highpass impulse response, highpass magnitude response, and filtered signal:
% --- Executes on button press in pbHighpass. function pbHighpass_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pbHighpass (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) global x; % Reads all filter spesifications As = str2num(get(handles.As,'String')); ws = str2num(get(handles.omega_s,'String')); Rp = str2num(get(handles.Rp,'String')); wp = str2num(get(handles.omega_p,'String')); ws=ws*pi; wp=wp*pi; bandwidth = ws - wp; M = ceil(6.6*pi/bandwidth) + 1; n=[0:1:M-1]; wc = (ws+wp)/2; % cutoff frequency of HPF % Choosing option from popup menu switch get(handles.popupmenuwindow,'Value') case 1 j=boxcar(M); case 2 j=bartlett(M); case 3 j=hann(M); case 4 j=hamming(M); case 5 j=blackman(M); case 6 beta = 0.1102*(As-8.7); j=kaiser(M,beta); end hd = ideal_lp(pi,M) - ideal_lp(wc,M); h = hd' .* j; [db,mag,pha,grd,w] = freqz_m(h,[1]); delta_w = 2*pi/1000; % Actual ripple passband Rp = -(min(db(1:1:wp/delta_w+1))); % Minimal stopband attenuation As = -round(max(db(ws/delta_w+1:1:501))); axes(handles.axes7); stem(n,hd, 'color','w'); title('Ideal Highpass Impulse Response') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axis([0 M-1 min(hd) max(hd)]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('hd(n)') axes(handles.axes8); stem(n,j,'color','w');title('Window Function') axis([0 M-1 0 1.1]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('w(n)') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axes(handles.axes9); stem(n,h,'color','w');title('Actual Highpass Impulse') axis([0 M-1 min(h) max(h)]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('h(n)') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axes(handles.axes3); plot(w/pi,db, 'linewidth',2,'color','y'); title('Magnitude Response in dB');grid axis([0 1 min(db) max(db)]); xlabel('Frequency in pi unit'); ylabel('dB') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); % Calculates filtered signal y = conv(double(x),double(h), 'same'); axes(handles.axes2); t = 0:length(y)-1; stem(t,y,'linewidth',1,'color','g'); title('Filtered Signal') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]);
11. You can run the UI. Choose one of signals and then click DRAW button, choose one of window functions, and click on Highpass button. The result is shown in figure below.
12. Right click on Bandpass button and choose View Callbacks and then choose Callback. Define pbBandpass_Callback() function below to read signals parameters and displays ideal bandpass impulse response, window function (based on window chosen from popupmenuwindow component), actual bandpass impulse response, bandpass magnitude response, and filtered signal:
% --- Executes on button press in pbBandpass. function pbBandpass_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pbBandpass (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) global x; % Reads all filter spesifications As = str2num(get(handles.As,'String')); ws = str2num(get(handles.omega_s,'String')); Rp = str2num(get(handles.Rp,'String')); wp = str2num(get(handles.omega_p,'String')); wp2 = str2num(get(handles.wp2,'String')); ws2 = str2num(get(handles.ws2,'String')); ws=ws*pi; wp=wp*pi; wp2=wp2*pi; ws2=ws2*pi; bandwidth = min((ws-wp),(ws2-wp2)); M = ceil(11*pi/bandwidth) + 1; n=[0:1:M-1]; wc1 = (ws+wp)/2; wc2 = (wp2+ws2)/2; % Choosing option from popup menu switch get(handles.popupmenuwindow,'Value') case 1 j=boxcar(M); case 2 j=bartlett(M); case 3 j=hann(M); case 4 j=hamming(M); case 5 j=blackman(M); case 6 beta = 0.1102*(As-8.7); j=kaiser(M,beta); end % Bandpass hd = ideal_lp(wc2,M) - ideal_lp(wc1,M); h = hd' .* j; [db,mag,pha,grd,w] = freqz_m(h,[1]); delta_w = 2*pi/1000; % Actual ripple passband Rp = -(min(db(1:1:wp/delta_w+1))); % Minimal stopband attenuation As = -round(max(db(ws/delta_w+1:1:501))); axes(handles.axes7); stem(n,hd, 'color','w'); title('Ideal Bandpass Impulse Response') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axis([0 M-1 min(hd) max(hd)]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('hd(n)') axes(handles.axes8); stem(n,j,'color','w');title('Window Function') axis([0 M-1 0 1.1]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('w(n)') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axes(handles.axes9); stem(n,h,'color','w');title('Actual Bandpass Impulse') axis([0 M-1 min(h) max(h)]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('h(n)') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axes(handles.axes3); plot(w/pi,db, 'linewidth',2,'color','y'); title('Magnitude Response in dB');grid axis([0 1 min(db) max(db)]); xlabel('Frequency in pi unit'); ylabel('dB') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); % Calculates filtered signal y = conv(double(x),double(h), 'same'); axes(handles.axes2); t = 0:length(y)-1; stem(t,y,'linewidth',1,'color','g'); title('Filtered Signal') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]);
13. You can run the UI. Choose one of signals and then click DRAW button, choose one of window functions, and click on Bandpass button. The result is shown in figure below.
14. Right click on Bandstop button and choose View Callbacks and then choose Callback. Define pbBandstop_Callback() function below to read signals parameters and displays ideal bandstop impulse response, window function (based on window chosen from popupmenuwindow component), actual bandstop impulse response, bandstop magnitude response, and filtered signal:
% --- Executes on button press in pbBandpass. function pbBandpass_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pbBandpass (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) % --- Executes on button press in pbBandstop. function pbBandstop_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pbBandstop (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) global x; % Reads all filter spesifications As = str2num(get(handles.As,'String')); ws = str2num(get(handles.omega_s,'String')); Rp = str2num(get(handles.Rp,'String')); wp = str2num(get(handles.omega_p,'String')); wp2 = str2num(get(handles.wp2,'String')); ws2 = str2num(get(handles.ws2,'String')); ws=ws*pi; wp=wp*pi; wp2=wp2*pi; ws2=ws2*pi; As = 60; tr_width = min((ws-wp),(ws2-wp2)); M = ceil(11*pi/tr_width) + 1; n=[0:1:M-1]; wc1 = (ws+wp)/2; wc2 = (wp2+ws2)/2; % Choosing option from popup menu switch get(handles.popupmenuwindow,'Value') case 1 j=boxcar(M); case 2 j=bartlett(M); case 3 j=hann(M); case 4 j=hamming(M); case 5 j=blackman(M); case 6 beta = 0.1102*(As-8.7); j=kaiser(M,beta); end % Bandstop hd = ideal_lp(wc1,M) + ideal_lp(pi,M) - ideal_lp(wc2,M); h = hd' .* j; [db,mag,pha,grd,w] = freqz_m(h,[1]); delta_w = 2*pi/1000; % Actual ripple passband Rp = -(min(db(1:1:wp/delta_w+1))); % Minimal stopband attenuation As = -round(max(db(ws/delta_w+1:1:501))); axes(handles.axes7); stem(n,hd, 'color','w'); title('Ideal Bandstop Impulse Response') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axis([0 M-1 min(hd) max(hd)]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('hd(n)') axes(handles.axes8); stem(n,j,'color','w');title('Window Function') axis([0 M-1 0 1.1]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('w(n)') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axes(handles.axes9); stem(n,h,'color','w');title('Actual Bandstop Impulse') axis([0 M-1 min(h) max(h)]); xlabel('n'); ylabel('h(n)') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); axes(handles.axes3); plot(w/pi,db, 'linewidth',2,'color','y'); title('Magnitude Response in dB');grid axis([0 1 min(db) max(db)]); xlabel('Frequency in pi unit'); ylabel('dB') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]); % Calculates filtered signal y = conv(double(x),double(h), 'same'); axes(handles.axes2); t = 0:length(y)-1; stem(t,y,'linewidth',1,'color','g'); title('Filtered Signal') set(gca,'color',[0.6,0.2,0.1]);
15. You can run the UI. Choose one of signals and then click DRAW button, choose one of window functions, and click on Bandstop button. The result is shown in figure below.
16. Right click on LOAD AUDIO FILE button and choose View Callbacks and then choose Callback. Define pbLoadAudioFile_Callback() function below to read audio file and display its spectrum:
% --- Executes on button press in pbLoadAudioFile. function pbLoadAudioFile_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pbLoadAudioFile (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) global x_audio; [filename,path] = uigetfile({'*.wav'},'Muat File Wav'); [x,Fs] = audioread([path '/' filename]); handles.x = x ./ max(abs(x)); handles.Fs = Fs; axes(handles.axes2); waktu = 0:1/Fs:(length(handles.x)-1)/Fs; plot(waktu, handles.x,'linewidth',1,'color','r'); set(gca,'color',[0.1,0.2,0.8]); axis([0 max(waktu) -1 1]); title('Audio Signal'); axes(handles.axes3); specgram(handles.x, 1024, handles.Fs); set(gca,'color',[0.2,0.2,0.8]); title('Signal Spectrum'); handles.fileLoad = 1; handles.fileNoise = 0; handles.fileFinal = 0; set(handles.SamplingFreq, 'String', num2str(Fs)); set(handles.NSamples, 'String', num2str(length(handles.x))); x_audio = handles.x; guidata(hObject, handles);
17. You can run the UI. Click LOAD AUDIO FILE button. The result is shown in figure below.
18. Right click on LPF AUDIO button and choose View Callbacks and then choose Callback. Define pbLPFAudio_Callback() function below to calculate and display filtered signal and its spectrum:
% --- Executes on button press in pbLPFAudio. function pbLPFAudio_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pbLPFAudio (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) global x; global x_audio; % Reads all filter spesification As = str2num(get(handles.As,'String')); ws = str2num(get(handles.omega_s,'String')); Rp = str2num(get(handles.Rp,'String')); wp = str2num(get(handles.omega_p,'String')); ws=ws*pi; wp=wp*pi; tr_width = ws - wp; M = ceil(6.6*pi/tr_width) + 1; n=[0:1:M-1]; wc = (ws+wp)/2; % Choose window function switch get(handles.popupmenuwindow,'Value') case 1 j=boxcar(M); case 2 j=bartlett(M); case 3 j=hann(M); case 4 j=hamming(M); case 5 j=blackman(M); case 6 beta = 0.1102*(As-8.7); j=kaiser(M,beta); end hd = ideal_lp(wc,M); h = hd' .* j; % Calculates filtered signal y = conv(hd,x_audio); axes(handles.axes2); t = 0:length(y)-1; plot(t,y,'linewidth',1,'color','r'); title('Filtered Signal') set(gca,'color',[0.1,0.2,0.8]); axes(handles.axes3) specgram(y, 1024, handles.Fs); title('Signal Spectrum'); handles.fileLoad = 1; set(gca,'color',[0.1,0.2,0.8]); handles.x=y; guidata(hObject, handles);
19. You can run the UI. Click LOAD AUDIO FILE button and then click LPF Audio button. The result is shown in figure below.
20. Right click on HPF AUDIO button and choose View Callbacks and then choose Callback. Define pbHPFAudio_Callback() function below to calculate and display filtered signal and its spectrum:
% --- Executes on button press in pbHPFAudio. function pbHPFAudio_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pbHPFAudio (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) global x; global x_audio; % Reads all filter spesification As = str2num(get(handles.As,'String')); ws = str2num(get(handles.omega_s,'String')); Rp = str2num(get(handles.Rp,'String')); wp = str2num(get(handles.omega_p,'String')); % Calculates cutoff frequency bandwidth = ws - wp; M = ceil(6.6*pi/bandwidth) + 1; n=[0:1:M-1]; wc = (ws+wp)/2; % Choose window function switch get(handles.popupmenuwindow,'Value') case 1 j=boxcar(M); case 2 j=bartlett(M); case 3 j=hann(M); case 4 j=hamming(M); case 5 j=blackman(M); case 6 beta = 0.1102*(As-8.7); j=kaiser(M,beta); end % HPF hd = ideal_lp(pi,M) - ideal_lp(wc,M); h = hd' .* j; % Calculates filtered signal y = conv(h,x_audio); axes(handles.axes2); t = 0:length(y)-1; plot(t,y,'linewidth',1,'color','r');title('Filtered Signal') set(gca,'color', [0.1,0.2,0.8]); axes(handles.axes3) specgram(y, 1024, handles.Fs); title('Spektrum Sinyal'); handles.fileLoad = 1; set(gca,'color', [0.1,0.2,0.8]); handles.x=y; guidata(hObject, handles);
21. You can run the UI. Click LOAD AUDIO FILE button and then click HPF Audio button. The result is shown in figure below.